Meta
这篇文章的作者和
H. Shin, L. Lu, L. Kim, A. Seff, J. Yao, and R. Summers. Interleaved text/image deep mining on a large-scale radiology
database. Proc. of IEEE CVPR, 2015.
有很大重复。
都是医院研究者搞的。
实验部分好多网络结构信手拈来,想必是玩了好久的练级高手了。
Intro
在最后一段,介绍本文三个微小的工作的时候,作者将第一个定为:joint mining of deep image features and labels,也就是题目了,其实这就是 iterative 优化 特征学习+聚类,没啥大不了的。
框架
第三节序言中,作者归纳道,对于 将medical records stored in the PACS into image labels or tags这个任务,作者的approach就是: iterative optimization process
- deep image feature extraction and clustering;
- deep CNN model fine-tuning (i.e., using new labels from clustering), to update deep feature extraction in the next round
强调一下,本文目标是 medical image categorization。
框架:
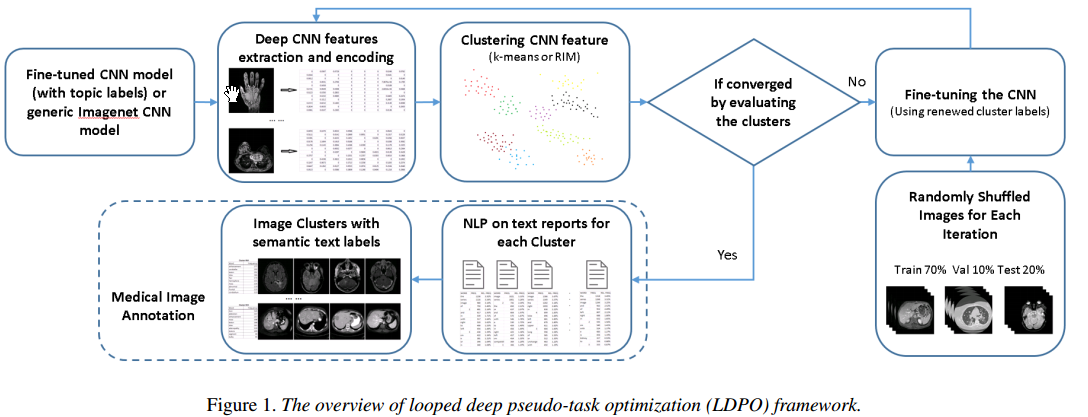
注意,特征提取之后 用k-means+RIM 就行了。
根据啥来停止iteration?
purity and mutual information between formed clusters in consecutive rounds
用啥来fine-tune?
uses the newly refined image cluster labels to train or fine-tune the CNN model in the next iteration
3.1 节的各种 Representation & Encoding 看不懂……
要想看懂这个,估计得把第二节Related Work那一部分好好看看了。
No way!
3.2 节 聚类
这一节聚类是重点。
又见到了熟悉的味道:先用k-means clustering to initialize the RIM clustering with a considerably large k。
这么做的理由当然是由于k-means的 $k$ 不好确定啦。
RIM (Discriminative clustering by regularized information maximization. NIPS, 2010)我是第一次听说。
它做的是 discriminative clustering,原理就是,通过一个模型复杂度的正则化项,来最大化 这俩货 data distribution and the resulted categories的互信息。
目标函数:

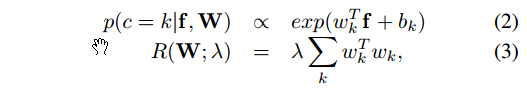
最大化目标函数等价于 solving a logistic regression problem
$\lambda$ 越大,类数越少。
实验部分
效果貌似不错,不过好多术语不清楚,不做评价。