以下来自:
[1]SPANGENBERG R, GOEHRING D, ROJAS R. Pole-based localization for autonomous vehicles in urban scenarios[C]//2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016: 2161–2166.
摘要
本文:
- 将 pole-like landmarks 作为 primary features,因为这些 pole-like landmarks, distinct, long-term stable and can be detected reliably with a stereo camera system
- 将 a stereo camera system 作为 main sensor
- 将 vehicle odometry 和 GPS 作为 secondary information sources
- 定位 使用 particle filter 和 Kalman filter 的耦合
- lateral accuracy below 20cm
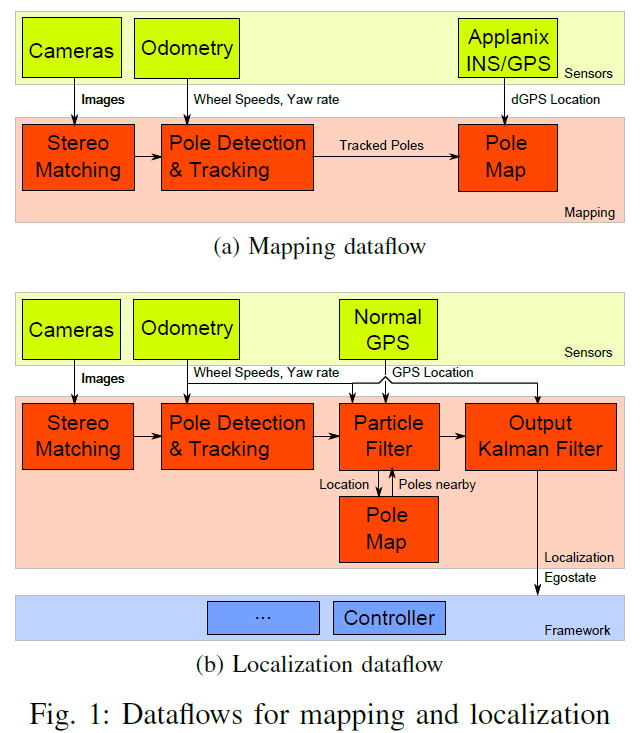
总览
- 建图阶段,根据rSGM 算法得到的disparity map进行Pole detection and tracking 。
- GPS 为 particle filter 提供初始化,然后 particle filter 根据 landmark 进行更新。
- 输出端使用 Kalman filter 来 隐藏计算延迟,并保证 100 Hz update rate。
- 定位结果可直接用于behavior planning and low-level control。
定位
粒子滤波部分
车辆的姿态估计 $\text{p}$ 由Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM)坐标系中, k 时刻的诸多粒子 $\text{p}_{k}^{i}$ 表示:
\(\text{p}_{k}^{i}=[E_{i}N_{i}\psi_{i}]^{T}\)
预测方程:
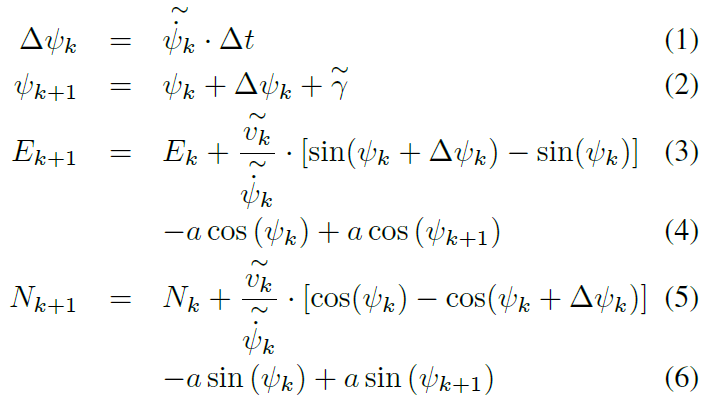
似然计算以及重采样略过。
卡尔曼滤波部分
为了保证robustness,以及smooth state estimation with an update rate of 100 Hz。
卡尔曼滤波器的状态为:
\(\mathbf{x}=(x,\ y,\ \psi,\ v,\dot{\psi})^{\text{T}}\)
vehicle dynamics采用Constant Turn Rate and Velocity Model (CTRV)。
在各路传感器输入的频率都很低的情况下,如何保证最终的输出是高频率的呢?
The Kalman filter includes all results as soon as they are available, time stamping makes sure that the filter is updated correctly, partially redoing calculations if measurements arrive too late.
The output is generated independently from the sensor input by filter prediction.
为了避免粒子滤波估计的车辆姿态出现sudden jumps,对其输出施加了一个validation gate,即抛弃掉明显不合理的输出,此时仅使用odometry measurements。
实验部分
作者着重算法的可重复性。
在同一路段,跑很多圈,并记录每次的定位结果。
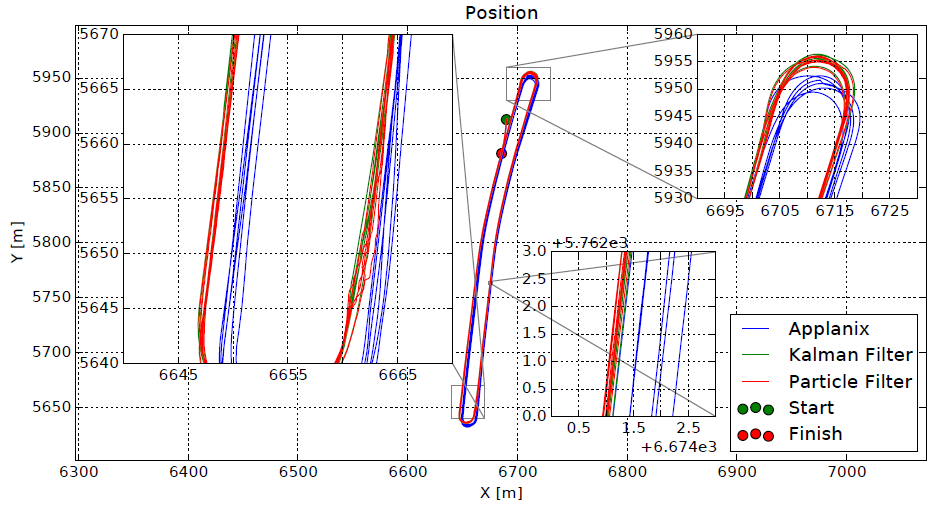
可以看到,粒子滤波在某些地方会出现跳变,经过卡尔曼滤波之后更smooth,而传感器的原始数据Applanix的可重复性最差。